These options are located in the Theme Options > Labels tab.
Labels options control the translation of text and the value of aria-label attributes. (Fig. 1)
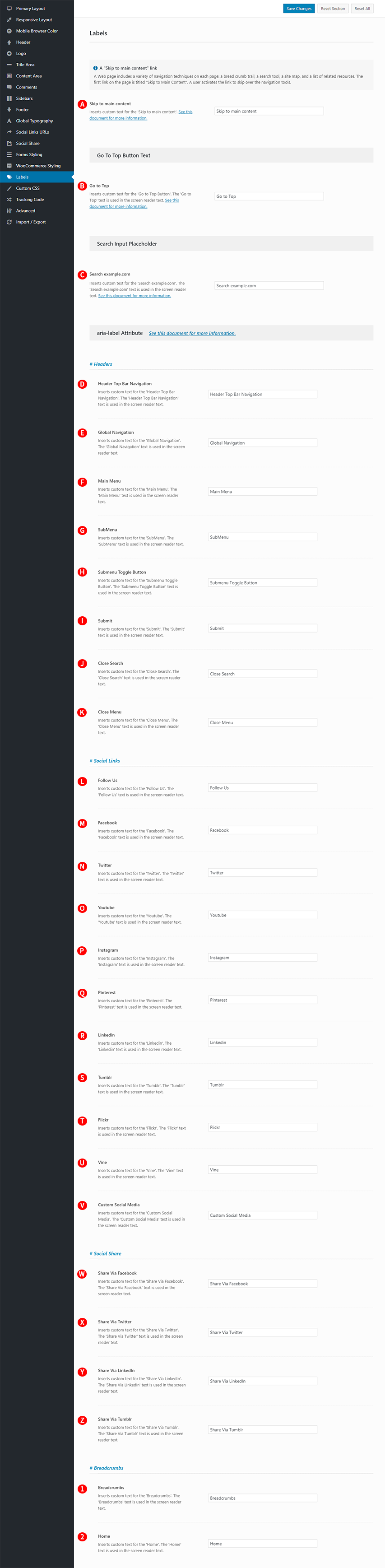
Skip to main content – Illustrated as A. Inserts custom text for the ‘Skip to main content’. (Fig. 2)
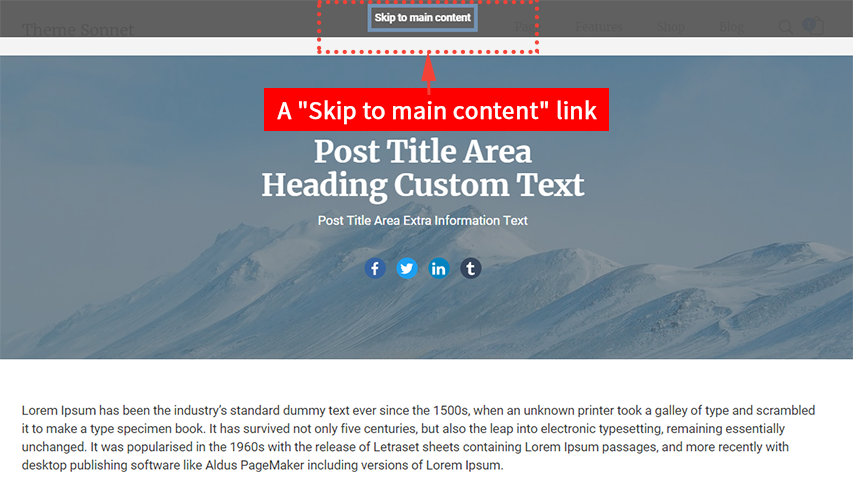
What is a ‘Skip to main content’ link?
A ‘Skip to main content’ link appears on the screen when the user presses the ‘tab’ key on the keyboard after the page loads.
A Web page includes a variety of navigation techniques on each page: a bread crumb trail, a search tool, a site map, and a list of related resources. The first link on the page is titled “Skip to Main Content”. A user activates the link to skip over the navigation tools.
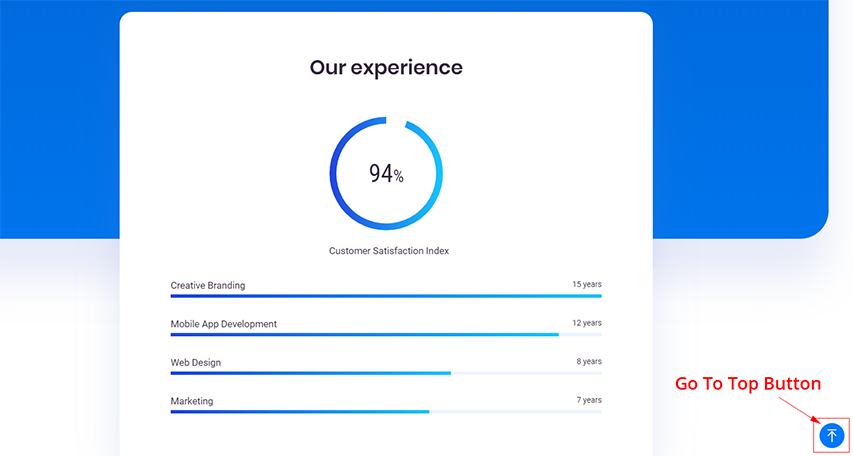
Go To Top Button Text
Go to Top – Illustrated as B. Inserts custom text for the ‘Go to Top Button’. The ‘Go to Top’ text is used in the screen reader text.
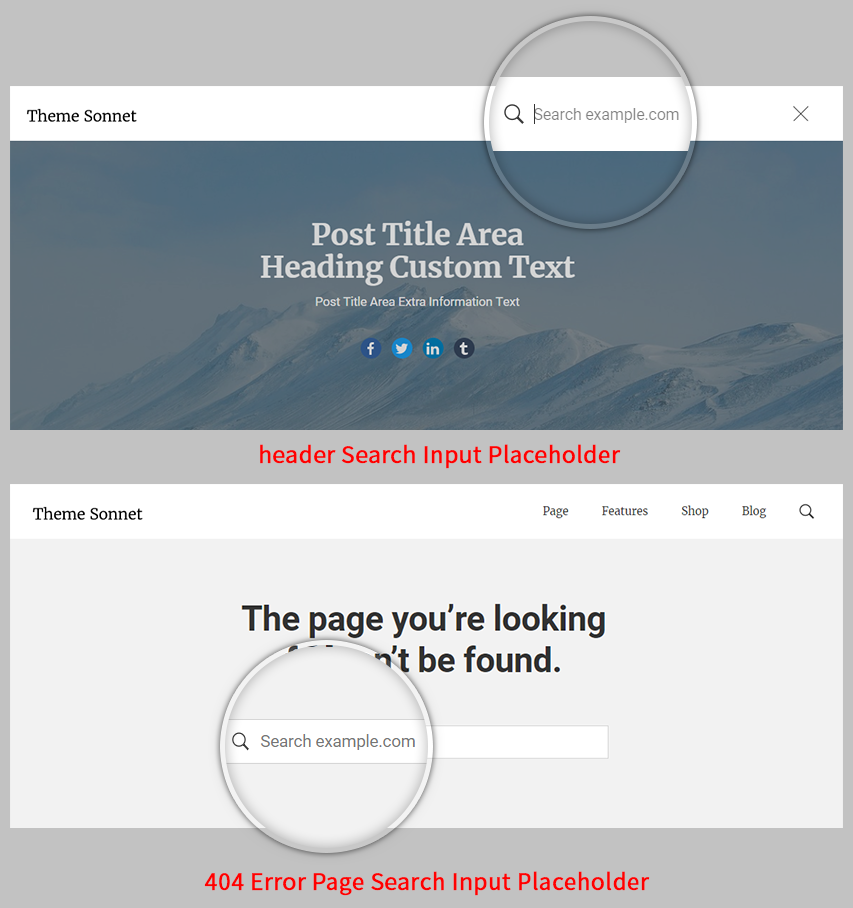
Search Input Placeholder
Search example.com – Illustrated as C. Inserts custom text for the ‘Search example.com’. The ‘Search example.com’ text is used in the screen reader text.
This custom text applies to placeholder text such as the search input box of the desktop header, the search input box of the mobile headers, the search input box of the 404 error page, the search input box of the search page and so on. (Fig. 4)
aria-label Attribute
Sonnet supports the best web accessibility and Sonnet is WCAG 2.0 compliant and ready.
What is a aria-label Attribute?
A aria-label Attribute is a very important technology for web accessibility.
Blind people get help from screen reader when they access the web. Screen reader read web content verbally to people who are blind, which is to tell them what it is when they read the relevant web content.
For example, when the screen reader reads the ‘Header Top Bar Navigation’ content area, it tells a blind person that it is ‘Header Top Bar Navigation’. If this technology is not applied, the screen reader will not be able to read it to the visually impaired because he or she does not know what the “Header Top Bar Navigation” content area means. This is so unfortunate for people who are blind.
# Headers
# Social Links
Follow Us – Illustrated as L. Inserts custom text for the ‘Follow Us’. The ‘Follow Us’ text is used in the screen reader text.
Facebook – Illustrated as M. Inserts custom text for the ‘Facebook’. The ‘Facebook’ text is used in the screen reader text.
Twitter – Illustrated as N. Inserts custom text for the ‘Twitter’. The ‘Twitter’ text is used in the screen reader text.
Youtube – Illustrated as O. Inserts custom text for the ‘Youtube’. The ‘Youtube’ text is used in the screen reader text.
Instagram – Illustrated as P. Inserts custom text for the ‘Instagram’. The ‘Instagram’ text is used in the screen reader text.
Pinterest – Illustrated as Q. Inserts custom text for the ‘Pinterest’. The ‘Pinterest’ text is used in the screen reader text.
Linkedin – Illustrated as R. Inserts custom text for the ‘Linkedin’. The ‘Linkedin’ text is used in the screen reader text.
Tumblr – Illustrated as S. Inserts custom text for the ‘Tumblr’. The ‘Tumblr’ text is used in the screen reader text.
Flickr – Illustrated as T. Inserts custom text for the ‘Flickr’. The ‘Flickr’ text is used in the screen reader text.
Vine – Illustrated as U. Inserts custom text for the ‘Vine’. The ‘Vine’ text is used in the screen reader text.
Custom Social Media – Illustrated as V. Inserts custom text for the ‘Custom Social Media’. The ‘Custom Social Media’ text is used in the screen reader text.
# Social Share
# Breadcrumbs
Breadcrumbs – Illustrated as 1. Inserts custom text for the ‘Breadcrumbs’. The ‘Breadcrumbs’ text is used in the screen reader text.
Home – Illustrated as 2. Inserts custom text for the ‘Home’. The ‘Home’ text is used in the screen reader text.